1. 創新的永續建築設計流程 Advanced Sustainable Design Process
|
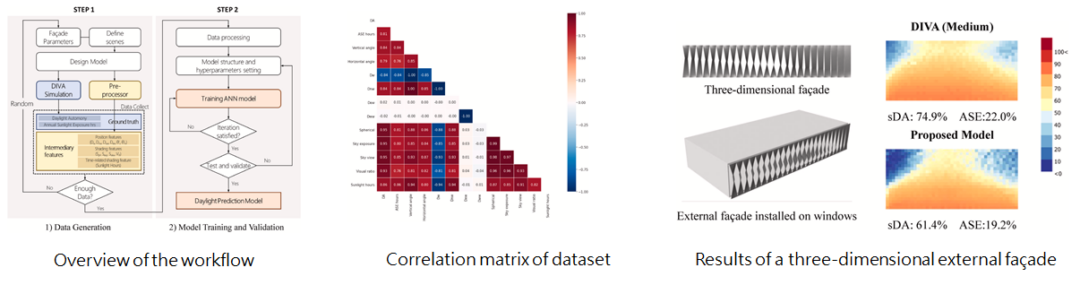
1-1 以機器學習模型方式進行建築立面日光設計的手法
|
A metamodel based on intermediary features for daylight performance prediction of façade design
Step 1: a novel daylight model, which includes a pre-processing procedure to convert the design model into “Intermediary features” as input parameters representing daylight penetration performance. Step 2: Daylight prediction models using machine learning methods. |
|
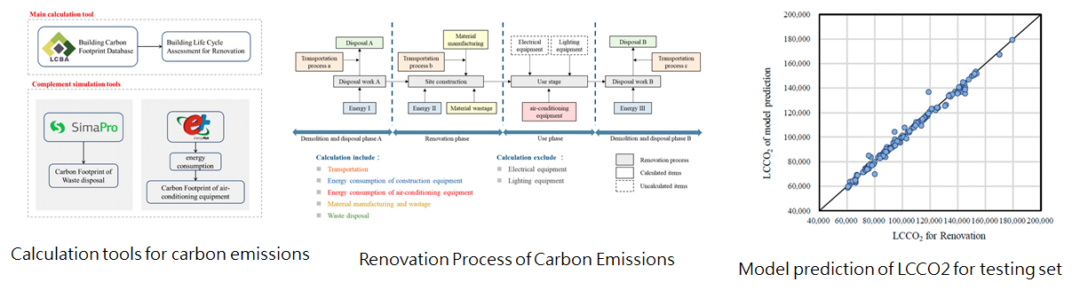
1-2 以機器學習方式預測住宅外殼更新之生命週期碳排放
|
A Machine Learning Based Prediction Model of LCCO2 for Building Envelope Renovation in Taiwan
|
|
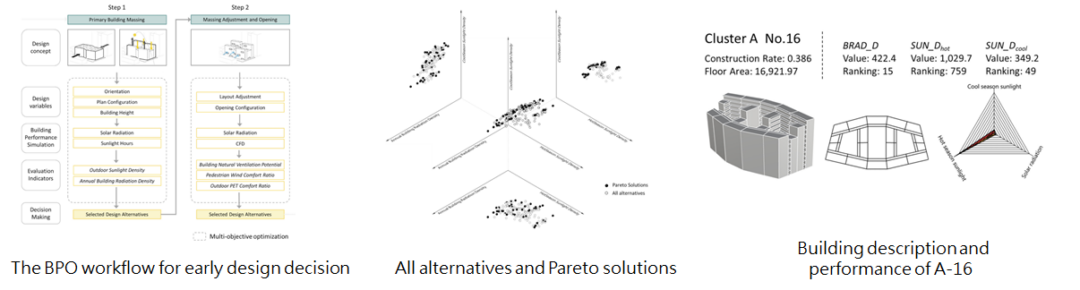
1-3 設計初期階段風環境與熱環境的多目的最佳化
|
Simulation Methodology Based on Wind and Thermal Performance for Early Building Optimization Design in Taiwan
|
|
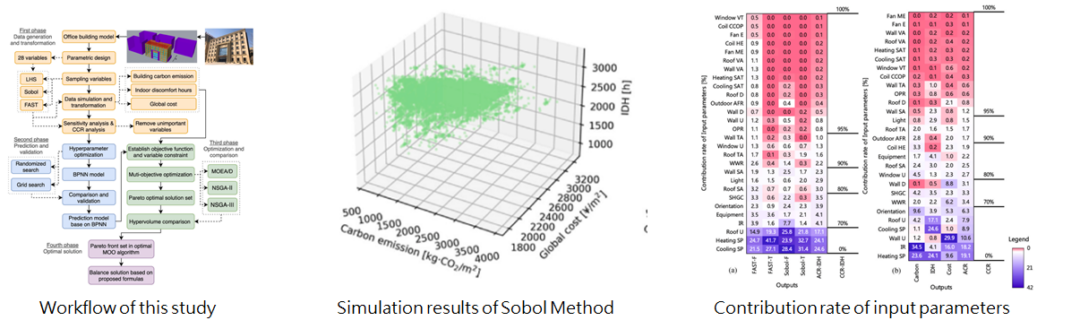
1-4 創新的整合式設計手法應用於建築耗能、熱舒適與建築成本之多目的最佳化分析
|
An integrated framework for multi-objective optimization of building performance: Carbon emissions, thermal comfort, and global cost
|
|
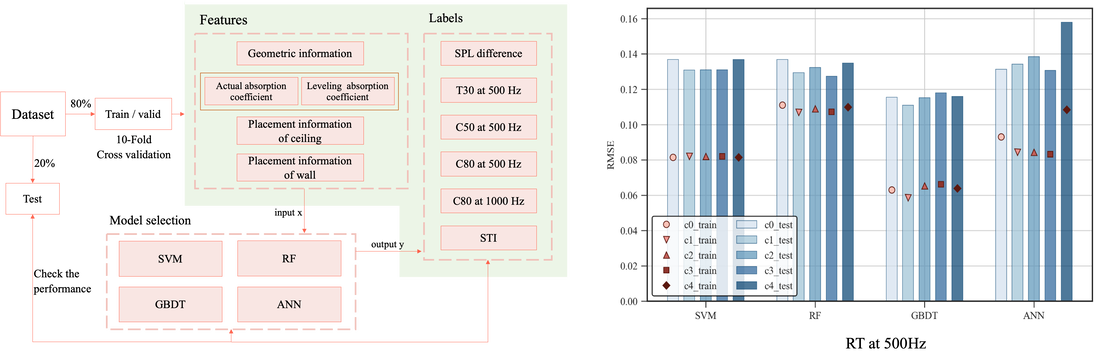
1-5 以機器學習手法快速預測室內聲學參數
|
Using Machine Learning to Predict Indoor Acoustic Indicators
|
2. 建築節能與低碳設計 Energy Conservation & Low-Carbon Design
|
2-1 金屬擴張網應用於建築立面設計
|
The Influence on Daylight and Energy Consumption of Expanded Metal Mesh Applied on Building Façades
|
|
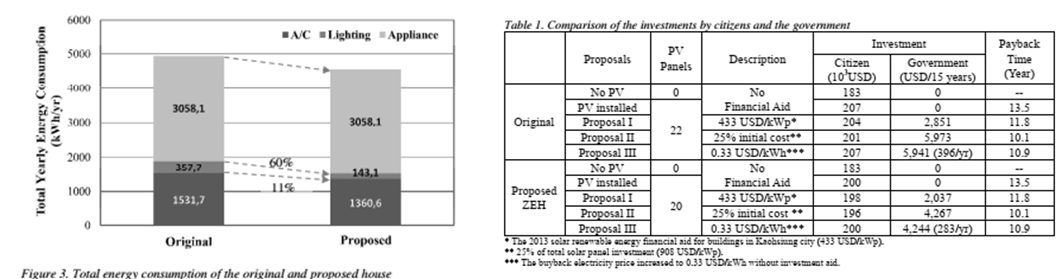
2-2 台灣氣候下的零耗能住宅設計
|
Strategies for ZEH Design in Taiwan
|
3. 健康居住環境與工作效率 Wellness & Productivity
|
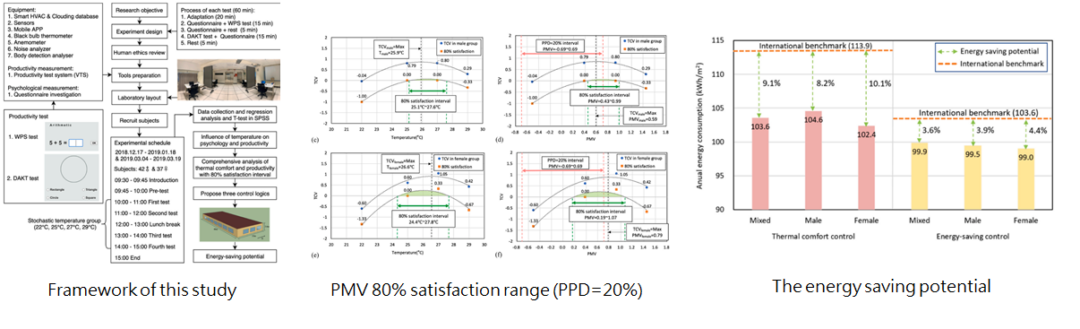
3-1 亞熱帶氣候下辦公建築兼顧熱舒適、工作效率與建築節能的潛力分析
|
Study on thermal comfort and energy conservation potential of office buildings in subtropical Taiwan
|
|
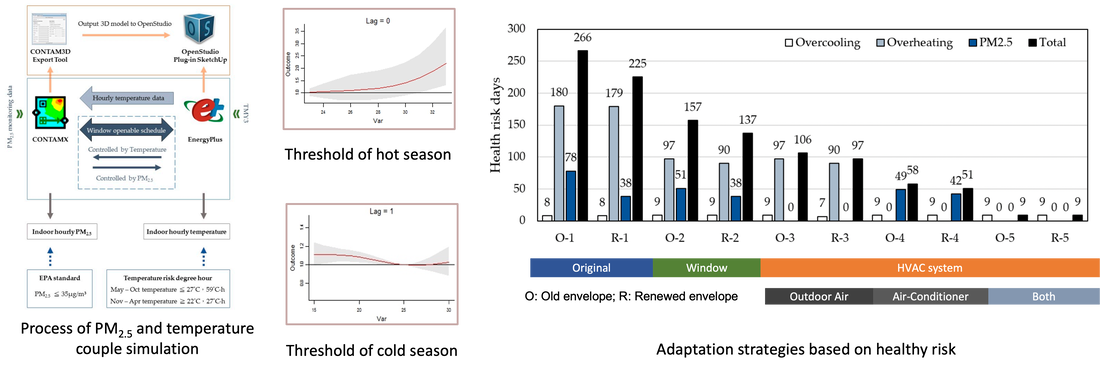
3-2 台灣街屋基於健康調適的設計策略分析
|
Adaptation Strategies of Residential Buildings Based on a Health Risk Evaluation—A Case Study of Townhouses in Taiwan
|
|
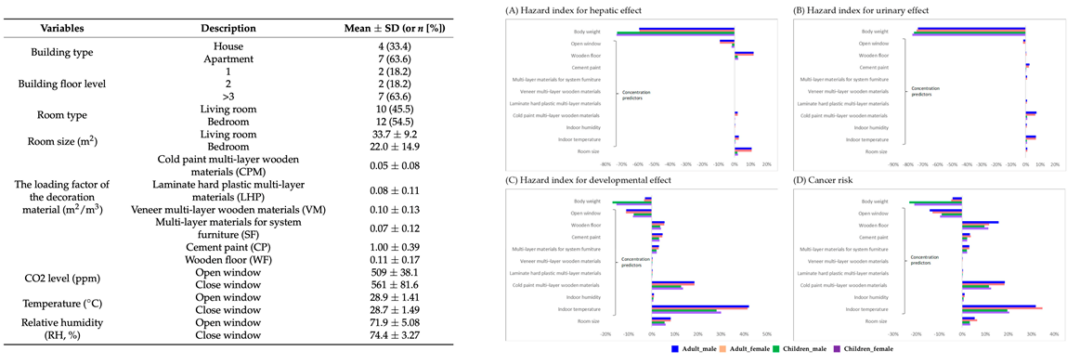
3-3 室內建材VOCs逸散與健康風險評估
|
Health Risk of VOCs Emission of Interior materials in Taiwan
|
|
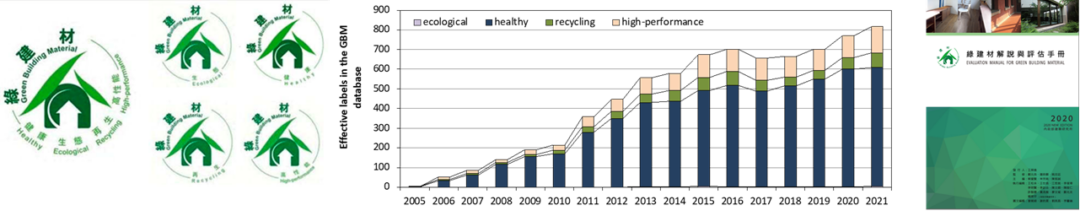
3-4 我國綠建材標章制度的推動
|
Green Building Material Labelling System in Taiwan
|
4. 建築立體綠化 Vertical Greenery System
|
4-1 窗台綠化對改善熱舒適環境的探討
|
Influence of Vertical Greening Design of Balconies and Opening of Buildings on Thermal Comfort
|
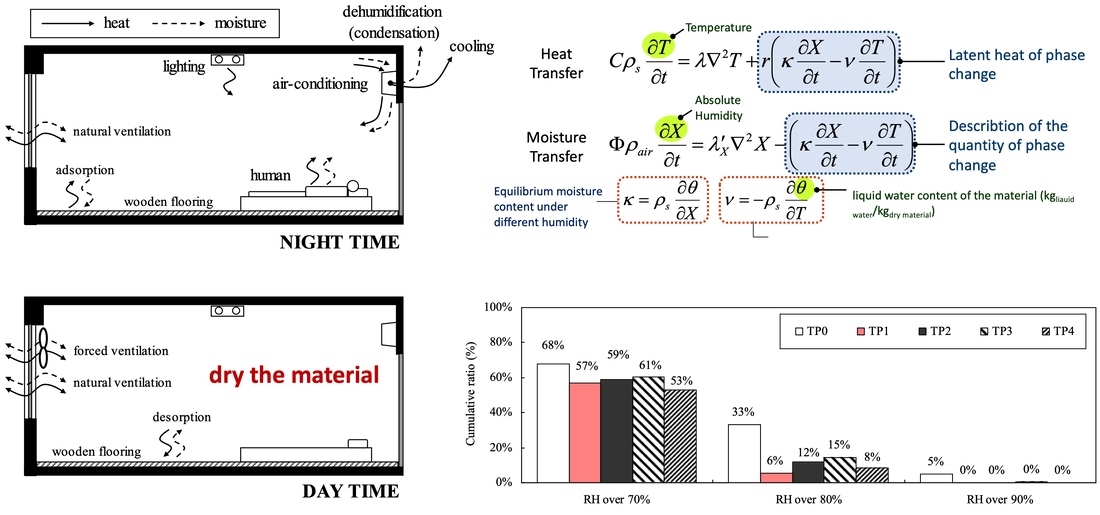
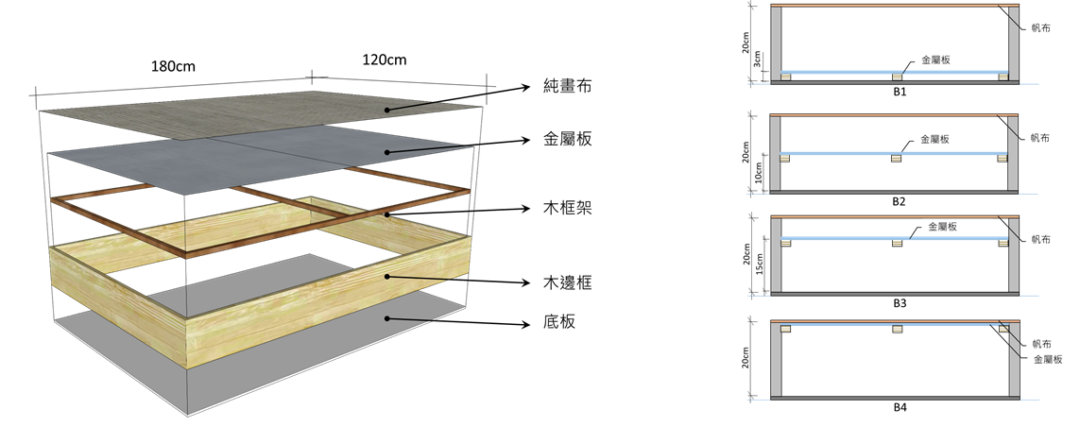
5. 調濕建材 Moisture Buffering Materials
|
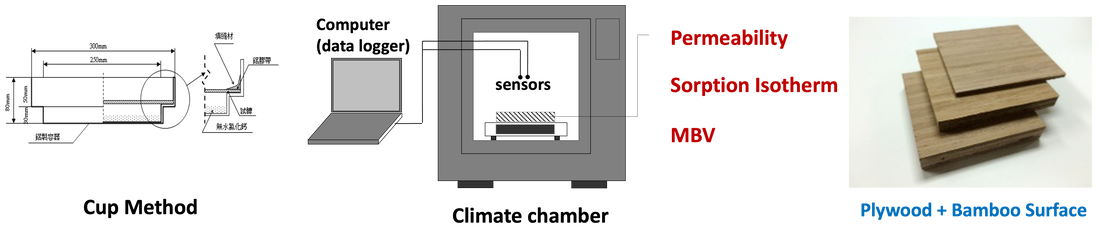
5-1 調濕建材基本物性的實驗分析
|
Hygro-thermal Properties of moisture buffering materials
|
|
5-2 台灣氣候下應用調濕建材的設計策略分析
|
Moisture buffering assessment applied in Taiwan
|
|
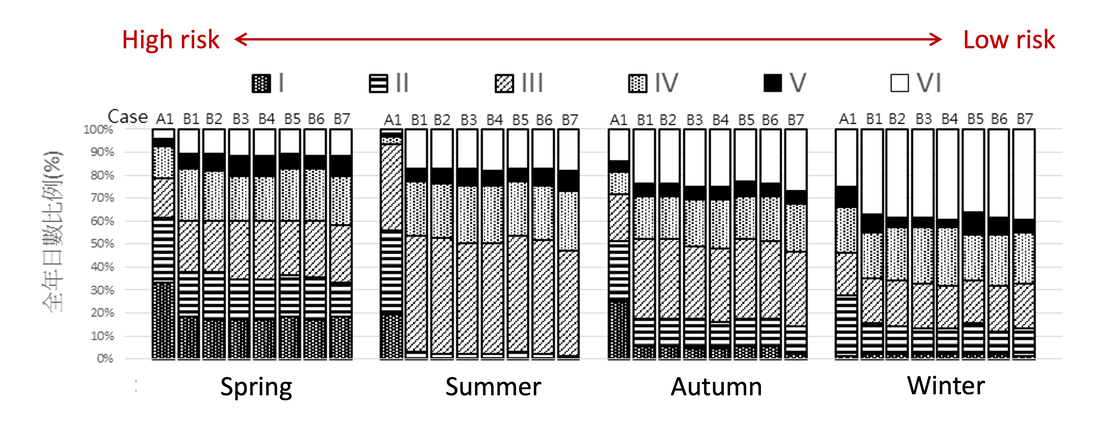
5-3 以黴菌發芽模型評估台灣氣候下調使用濕建材的效益
|
Evaluating moisture buffering effect via mold germination model
|
6. 建築聲學 Architectural Acoustics
|
6-1 摺板式金屬擴張網吸音板FEMM的開發
|
Development of Folded Expanded Metal Mesh (FEMM)
|
|
6-2 板膜共振吸音體PMRA的開發
|
Development of Panel Membrane Resonant Absorber (PMRA)
|
|
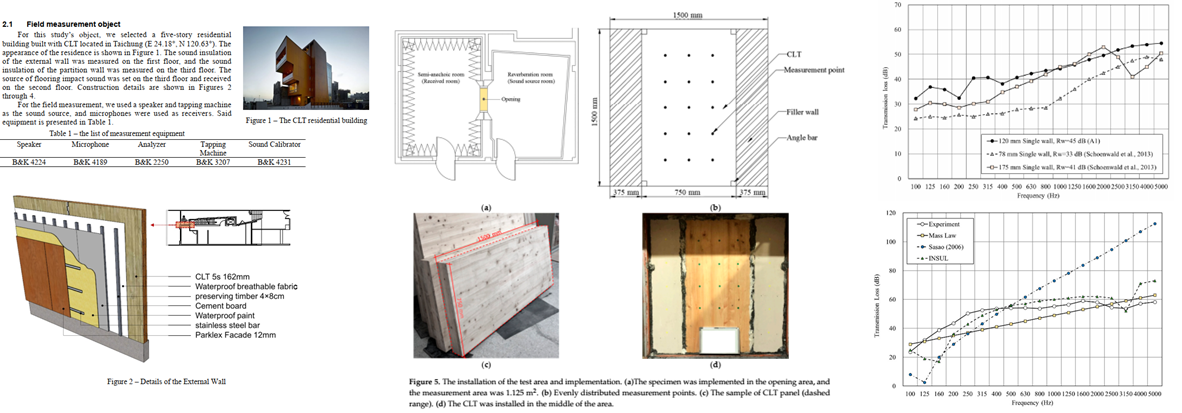
6-3 CLT牆體的隔音性能與預測模式
|
Sound Insulation Performance of Cross-laminated Timber (CLT)
|